Multiplexing is a technique used to combine and send the multiple data streams over a single medium. The process of combining the data streams is known as multiplexing and hardware used for multiplexing is known as a multiplexer.
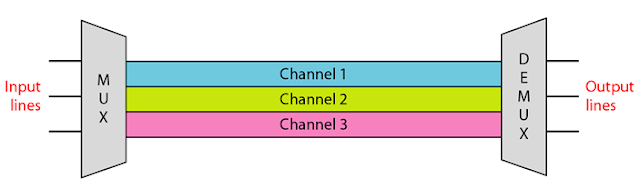
Multiplexing is achieved by using a device called Multiplexer (MUX) that combines n input lines to generate a single output line. Multiplexing follows many-to-one, i.e., n input lines and one output line.
Demultiplexing is achieved by using a device called Demultiplexer (DEMUX) available at the receiving end. DEMUX separates a signal into its component signals (one input and n outputs).
The transmission medium is used to send the signal from sender to receiver. The medium can only have one signal at a time. If there are multiple signals to share one medium, then the medium must be divided in such a way that each signal is given some portion of the available bandwidth.
For example: If there are 10 signals and bandwidth of medium is 100 units, then the 10 unit is shared by each signal.
When multiple signals share the common medium, there is a possibility of collision. Multiplexing concept is used to avoid such collision.
Types of Multiplexing
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) –
Frequency spectrum is divided among the logical channels and each user has exclusive access to his channel. It sends signals in several distinct frequency ranges and carries multiple video channels on a single cable. Each signal is modulated onto a different carrier frequency and carrier frequencies are separated by guard bands.
Bandwidth of the transmission medium exceeds required bandwidth of all the signals. Usually for frequency division multiplexing analog signalling is used in order to transmit the signals, i.e. more susceptible to noise.
A multiplexer accepts inputs and assigns frequencies to each device. The multiplexer is attached to the high speed communication line. A corresponding multiplexer or de-multiplexer is on the end of the high speed line and separates the multiplexed signals. The frequency spectrum is divided up among the logical channels where each user hangs onto a particular frequency. The radio spectrum are examples of the media and the mechanism for extracting information from the medium.


Disadvantage of FDM:
One problem with FDM is that it cannot utilize the full capacity of the cable. It is important that the frequency bands do not overlap. Indeed, there must be a considerable gap between the frequency bands in order to ensure that signals from one band do not effect signals in another band.
Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)
Each user periodically gets the entire bandwidth for a small burst of time, i.e. entire channel is dedicated to one user but only for a short period of time. It is very extensively used in computer communication and tele-communication. Sharing of the channel is accomplished by dividing available transmission time on a medium among users. It exclusively uses the Digital Signaling instead of dividing the cable into frequency bands.
TDM splits cable usage into time slots. Data rate of transmission media exceeds dats rate of signals. Uses a frame and one slot for each slice of time and the time slots are transmitted whether source has data or not.
There are two types of TDMs which are as follows:
1. Synchronous Time Division Multiplexing:
It is synchronous because the multiplexer and the de-multiplexer has to agree about the time slots. The original time division multiplexing. The multiplexer accepts input from attached devices in a round robin fashion and transit the data in a never ending pattern. Each input connection has an allotment even if it is not sending data.
Some common examples of this are T-1 and ISDN telephone lines.
One problem with TDM is to handle different data rates. Three techniques or combination are used to handle
a. Multilevel Multiplexing
b. Multiple-slot Multiplexing
c. Pulse stuffing.
Multilevel Multiplexing:
In this technique different data rates are handled by combining two or more input links into one link as shown in below figure.
Multiple-slot Multiplexing:
In this technique one data rate signal is split into two or more links as shown in below figure.
Pulse stuffing:
In this technique if a link has less data rate then pulse stuffing is done to make the data rate equal to other links as shown in the figure below.
2. Statistical Time Division Multiplexing:
Time-division but on demand rather than fixed, a slot is given in the output frame only if three input line has a slot's worth of data to send. It allows connection of more nodes to the circuit than the capacity of the circuit. Works on the premise that not all the nodes will transmit at full capacity at all times.
It must transmit a terminal identification i.e destination identification number, and may require storage. A statistical multiplexer transmits only the data from active workstations. If a workstation is not active, no space is wasted on the multiplexed stream. It accepts the incoming data streams and creates a frame containing only the data to be transmitted.
In statistical division multiplexing a slot needs to carry data as well as the address of destination.
Time Slot comparison of Syn TDM and Stat TDM











No comments:
Post a Comment